Sweep PropertyManager
Set the PropertyManager options based on the type of sweep feature.
See Sweep
Overview for more information about sweeps.
Profile and Path
|
Profile sweep. Creates a sweep
using a profile and path. |
|
|
|
|
Solid sweep (cut sweeps only).
Creates a cut-sweep using a tool body and path. The most common usage
is in creating cuts around cylindrical bodies. This option would also
be useful for end mill simulation.
For cut sweeps only, when you select Solid
sweep, the path must be tangent within itself (no sharp corners)
and begin at a point on or within the tool body profile. |
|
|
|
|
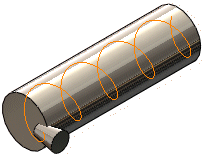
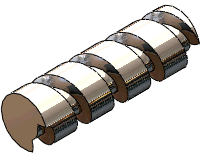
Tool body and path |
Cut sweep |
|
|
|
|
|
|
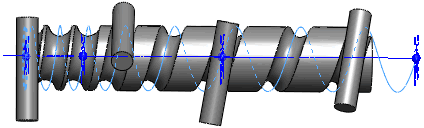
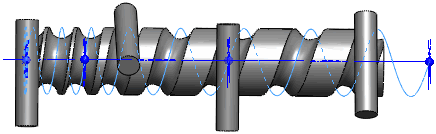
Note how Solid
sweep handles a tool body following a helix path:
When you select Follow
path for the Orientation/twist
type, and None for Path alignment type, the tool body correctly
follows the tangents of the helix path. |
|
|
|
|
|
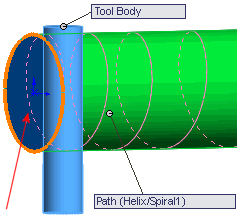
To keep the tool body perpendicular to a
reference as it follows a helix path, select Direction
Vector for Path alignment type,
then select a direction to which the tool body remains perpendicular,
for example, the normal to the planar end face of a cylinder. |
|
|
|
The tool body remains parallel to the end
face as it follows the helix path along the cylinder. This functionality
is important for the tool machining market. |
|
|
Profile
 . Sets the sketch profile (section) used to create the
sweep. Select the profile sketch in the graphics area or FeatureManager
design tree. The profile must be closed for a base or boss sweep feature.
The profile may be open or closed for a surface sweep feature.
. Sets the sketch profile (section) used to create the
sweep. Select the profile sketch in the graphics area or FeatureManager
design tree. The profile must be closed for a base or boss sweep feature.
The profile may be open or closed for a surface sweep feature.
Tool
body  (solid cut sweeps only). The tool body must:
(solid cut sweeps only). The tool body must:
Be
a 360-degree revolved feature.
Contain
only analytical geometry, such as lines and arcs
Not
be merged with the model.
Path
 . Sets the path along which the profile sweeps. Select
the path sketch in the graphics area or FeatureManager design tree. The
path can be open or closed, and can be a set of sketched curves contained
in one sketch, a curve, or a set of model edges. The start point of the
path must lie on the plane of the profile.
. Sets the path along which the profile sweeps. Select
the path sketch in the graphics area or FeatureManager design tree. The
path can be open or closed, and can be a set of sketched curves contained
in one sketch, a curve, or a set of model edges. The start point of the
path must lie on the plane of the profile.
 Neither the section, the path, nor the resulting solid can
be self-intersecting.
Neither the section, the path, nor the resulting solid can
be self-intersecting.
Options
 of Orientation/twist control
of Orientation/twist control
Path
alignment type (Available with Follow Path selected
in Orientation/twist type). Stabilizes
the profile when small and uneven curvature fluctuations along the path
cause the profile to misalign. Options are:
None. Aligns the profile normal to the
path. No correction is applied.
Minimum Twist (For 3D paths only). Prevents
the profile from becoming self-intersecting as it follows the path.
Direction Vector. Aligns the profile
in the direction selected for Direction
Vector. Select entities to set the direction vector.
All Faces. When the path includes adjacent
faces, makes the sweep profile tangent to the adjacent face where geometrically
possible.
Direction
Vector  (Available with Direction
Vector selected in Path alignment
type). Select a plane, planar face, line, edge, cylinder, axis,
a pair of vertices on a feature, and so on to set the direction vector.
(Available with Direction
Vector selected in Path alignment
type). Select a plane, planar face, line, edge, cylinder, axis,
a pair of vertices on a feature, and so on to set the direction vector.
Merge
tangent faces. If the sweep profile has tangent segments, causes
the corresponding surfaces in the resulting sweep to be tangent. Faces
that can be represented as a plane, cylinder, or cone are maintained.
Other adjacent faces are merged, and the profiles are approximated. Sketch
arcs may be converted to splines.
Show
preview. Displays a shaded preview of the sweep. Clear to display
only the profile and path.
Merge
result. Merges the solids into one body.
Align with end
faces. Continues the sweep profile up to the last face encountered
by the path. The faces of the sweep are extended or truncated to match
the faces at the ends of the sweep without requiring additional geometry.
This option is commonly used with helices. 
Guide Curves
 The guide curve must be coincident
with the profile or with a point in the profile sketch.
The guide curve must be coincident
with the profile or with a point in the profile sketch.
Start/End Tangency
Thin Feature
Select to create a thin feature
sweep. 
Feature
Scope
Apply features to one or more
multibody parts. Use Feature Scope
to choose which bodies should include the feature.
 of cut extrude feature scope
of cut extrude feature scope
 You must create the model to which you want to add the features
for multibody parts prior to adding those features.
You must create the model to which you want to add the features
for multibody parts prior to adding those features.
All
bodies. Applies the feature to all bodies every time the feature
regenerates. If you add new bodies to the model that are intersected by
the feature, these new bodies are also regenerated to include the feature.
Selected
bodies. Applies the feature to the bodies you select. If you add
new bodies to the model that are intersected by the feature, you need
to use Edit Feature to edit the
extrude feature, select those bodies, and to add them to the list of selected
bodies. If you do not add the new bodies to the list of selected bodies,
they remain intact.
Auto-select.
(Available if you click Selected bodies).
When you first create a model with multibody parts, the feature automatically
processes all the relevant intersecting parts. Auto-select
is faster than All bodies because
it processes only the bodies on the initial list and does not regenerate
the entire model. If you click Selected
bodies and clear Auto-select,
you must select the bodies in the graphics area you want to include.
Solid
Bodies to Affect  (Available if you clear Auto-select). Select the bodies to affect
in the graphics area.
(Available if you clear Auto-select). Select the bodies to affect
in the graphics area.