SolidWorks Sustainability evaluates
the environmental impact of a design throughout the life cycle of a product. You can compare
results from different designs to ensure a sustainable solution for
the product and the environment.
Two products are available:
- SolidWorks SustainabilityXpress
- Handles part documents (solid bodies only) and is included in the core software.
- SolidWorks Sustainability
- Handles parts (solid bodies only) and assemblies. Available as a separate product. Other functionality includes configuration support, expanded reporting, and expanded environmental impact options.
To begin working with SustainabilityXpress, click one of the following:
- SustainabilityXpress
 (Tools toolbar or Evaluate CommandManager tab)
(Tools toolbar or Evaluate CommandManager tab)
The application opens in the Task Pane.
Dashboard and Reports
SolidWorks Sustainability provides real-time feedback on environmental impact factors. Results appear in the Environmental Impact Dashboard, which updates dynamically with any changes.
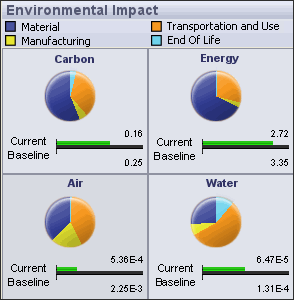
You can generate customizable reports to share the results.
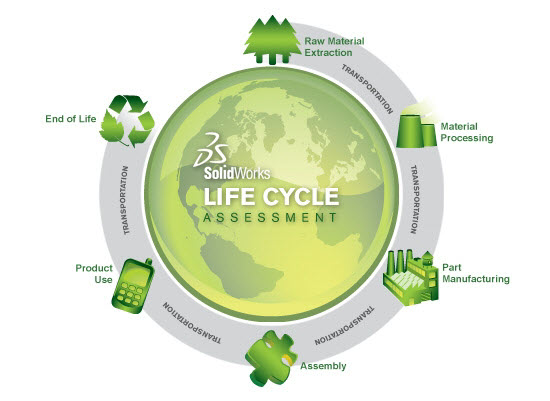
Life Cycle Assessment
By integrating Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) into the design process, you can see how decisions about material, manufacturing, and location (where parts are manufactured and where they are used) influence a design’s environmental impact. You specify various parameters that SolidWorks Sustainability uses to perform a comprehensive evaluation of all the steps in a design’s life.
LCA includes:
- Ore extraction from the earth
- Material processing
- Part manufacturing
- Assembly
- Product usage by the end consumer
- End of Life (EOL) – Landfill, recycling, and incineration
- All the transportation that occurs between and within each of these steps.
Environmental Impact Factors
SolidWorks Sustainability assesses all the life cycle steps based on your material, manufacturing, and location input. SolidWorks Sustainability distills the results into environmental impact factors, which it measures and totals.
- Carbon Emissions
- Carbon dioxide and equivalents, such as carbon monoxide and methane, that are released into the atmosphere, resulting in global warming.
- Energy Consumed
- All forms of energy consumed over the entire life cycle of the product.
- Air Acidification
- Air pollution primarily due to the burning of fossil fuels, eventually leading to acid rain.
- Water Eutrophication
- Contamination by fertilizers that travel through rivers to coastal waters, resulting in algae blooms and the eventual killing of all sea life in certain coastal regions.