You can select from four types of 2D simplification options based on the geometry, material properties, fixtures, loads, and contact conditions.
- Plane stress
Simulates thin geometries with no forces acting normal to the section plane. For the plane stress assumption, no stresses develop normal to the section plane. This option is available for static and nonlinear studies.
This examples shows a bracket under distributed load.
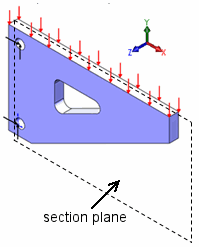
Other examples include thin plates under pressure, turning a wrench while tightening a bolt, and snap fit of plastic clips.
- Plane strain
Simulates thick geometries that extend a long distance on either side of the section plane with no forces acting normal to the section plane. For the plane strain assumption, no strains develop normal to the section plane. Plane strain problems are less common than plane stress problems. This option is not available for thermal studies.
This example shows a dam under water pressure.

Other examples include a tunnel under pressure and sheet rolling.
- Extruded
Simulates geometries with constant thermal loads along the extrusion direction. This option is available only for thermal studies.
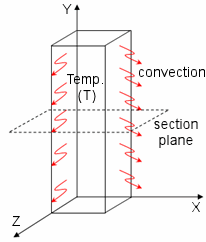
The figure shows an example of a long block held at a uniform temperature and suddenly exposed to a convection environment.
- Axisymmetric
Simulates geometries, material properties, loads, and fixtures that are symmetric about an axis. This example shows a nonlinear contact analysis of an o-ring.
| 3D geometry |
Modeled section |
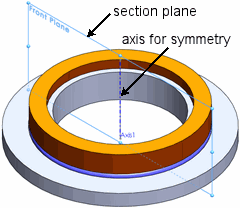 |
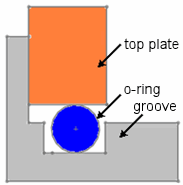 |
Other examples include vessels under external or internal pressure and many problems encountered in turbine construction.