Remote Load (Direct Transfer)
You can use this option when the omitted component is adequately flexible
but its displacements are still within the small displacement assumption.
Remote loads (forces and/or moments) are applied at a point defined by
the X-, Y-, and Z-locations in reference to a selected coordinate system.
The global coordinate system is used by default if no coordinate system
is selected. Remote moments are applied about the specified axes of the
coordinate system. The program automatically calculates and applies equivalent
forces to selected faces. A force applied at the remote location transfers
as a force and equivalent moment(s)
applied to selected face(s).
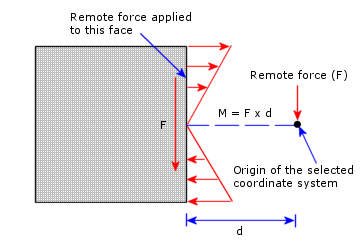
For example, if you apply a remote force F
to a face as shown in the figure, the program applies forces that are
equivalent to a moment M = F
x d in addition
to the force F.
 It is advisable to apply all remote force and moment
components ( X-, Y-, Z-direction with respect to a local coordinate system)
in one definition.
It is advisable to apply all remote force and moment
components ( X-, Y-, Z-direction with respect to a local coordinate system)
in one definition.
To apply a remote load (direct transfer) to a face:
In the Simulation study tree, right-click the
External Loads  icon
an select Remote Load/Mass
icon
an select Remote Load/Mass  .
.
Under Type,
select Load (Direct transfer).
In the graphics area, click the faces to which
you want to apply the remote load.
Under Reference
Coordinate System, select Global
(default global coordinate system), or User
defined.
Under Location,
do the following:
Select the desired Unit
for length  .
.
Type the coordinates of the point of application
of the remote force in the X-Location
 , Y-Location
, Y-Location  , and Z-Location
, and Z-Location  boxes.
boxes.
Under Force,
do the following:
Set Unit
 to the desired unit of force.
to the desired unit of force.
Click the force components that you want to
specify and type in their values.
Under Moment,
do the following:
Set Unit
 to the desired unit of moment.
to the desired unit of moment.
Click the moment components that you want
to specify and type in their values.
Click  .
.