Linear Elastic Isotropic Model
A material is said to be isotropic if its properties do not vary with direction. Isotropic materials therefore have identical elastic modulus, Poisson's ratio, coefficient of thermal expansion, thermal conductivity, etc. in all directions. The term isothermal is some times used to denote materials with no preferred directions for coefficients of thermal expansion.
In order to define the isotropic elastic properties, you must define the elastic modulus E
x . The program assumes a value of 0.0 for Poisson's ratio n
xy,if no specific value is specified. A common value for the Poisson's ratio is 0.3. The shear modulus G
xy. is calculated internally by the program even if it is explicitly specified.

The stiffness matrix for an isotropic material contains only two independent coefficients. The following sections describe the isotropic stress-strain relations in two- and three-dimensions including the effect of thermal strains.
Isotropic Stress-Strain Relations
The most general form of the isotropic stress-strain relations including thermal effects is shown below:
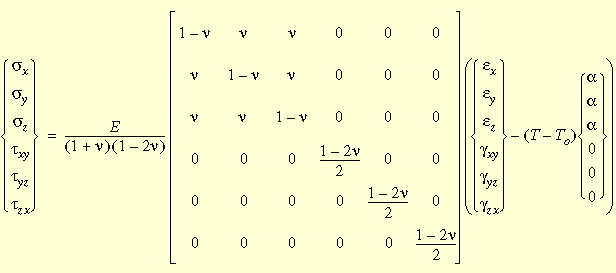
Assumptions of Linear Elastic Material Models
Linear elastic material models make the following assumptions:
-
Linearity Assumption. The induced response is directly proportional to the applied loads. For example, if you double the magnitude of loads, the model's response (displacements, strains, and stresses) will double. You can make the linearity assumption if the following conditions are satisfied:
-
The highest stress is in the linear range of the stress-strain curve characterized by a straight line starting from the origin. As the stress increases, materials demonstrate nonlinear behavior above a certain stress level. This assumption asserts that the stress should be below this level. Some materials, like rubber, demonstrate a nonlinear stress-strain relationship even for low stresses.
-
The maximum displacement is considerably smaller than the characteristic dimension of the model. For example, the maximum displacement of a plate must be considerably smaller than its thickness and the maximum displacement of a beam must be considerably smaller than the smallest dimension of its cross-section.
-
Elasticity Assumption. The loads do not cause any permanent deformation. In other words, the model is assumed to be perfectly elastic. A perfectly elastic model returns to its original shape when the loads are removed.
Isotropic vs. orthotropic materials