Stress Error
After calculating displacements at all nodes, the program proceeds to calculate strains and then stresses for each element independently. The stresses are calculated at certain points within each element. These points are strategically located within an element to provide accurate results. They are called Gaussian or quadrature points.
After calculating the stresses at the Gaussian points, the program calculates the nodal stresses for each element by extrapolation.
For an exact solution, all elements should give identical stress values at their common nodes. While the displacement field obtained by FEA is continuous, the stress field is usually discontinuous from one element to another. Different elements give stress values that are generally different at a common node. The program calculates the nodal stresses at a common node by averaging the values given by the contributing elements.
The variation in stresses at common nodes provides a measure for the accuracy of the solution based on strain energy principles. The software estimates the error distribution as follows:
Suppose that:
si*= stress at the common node from an associated element
s = average stress at the common node
The difference between the stress value calculated from an element at a common node and the average stress value is expressed as:
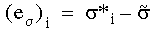
The error in energy norm for each element is calculated from:
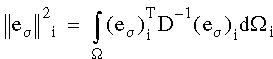
where D is the elasticity matrix and Wi is the element domain. A global error estimate is calculated by summing the errors from all elements:
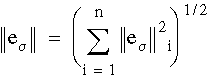
where n is the total number of elements. The percentage error for each element is calculated from:

where ||u|| is twice the total strain energy calculated from:
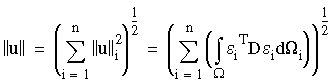
where e is the strain vector.
The quantity h
i is plotted when you set Result type to Element values and Component to ERR: Stress Energy in the
Stress Plot PropertyManager
. Note that the plotted error is an estimate of the error in energy norm and not in stresses. However, it can be viewed to represent the relative distribution of stress errors in homogeneous meshes. This quantity is used by the p-adaptive method to improve results at locations with higher energy errors.
For more information about error estimation, refer to International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, vol. 24, 337-357 (1987) “A Simple Error Estimator and Adaptive Procedure for Practical Engineering Analysis” by O.C. Zienkiewicz and J. Z. Zhu).