Deform Overview
Use the deform feature to alter shapes of complex surface or solid models, either in a local area or globally, without concern for the sketches or feature constraints used to create the models.
Deform provides a simple way to change virtually any model, whether organic or mechanical, and is useful when creating design concepts or making geometric changes to complex models that would otherwise take too long using traditional sketch, feature, or history editing.
You can apply the deform feature to both SolidWorks and imported models.
There are three deform types:
-
Point
-
Curve to curve
-
Surface push
Deform - Point
Point deform is the simplest way to alter complex shapes. Select a point on a model face, surface, edge, vertex, or select a point in space, then choose a distance and spherical radius by which to control the deformation.
You can also select additional faces and bodies if required. See Deform - Point Options for details on the PropertyManager options. For additional examples of deforming models with the point option, see Deform - Point Examples.
 Example of point on face deformation
Example of point on face deformation
|
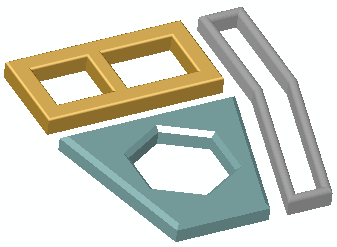
Example of point deformation on a multibody part
|
|
|
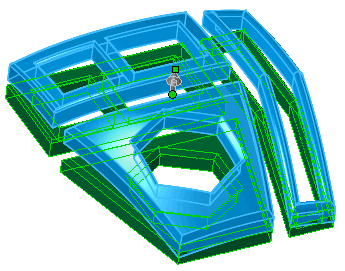
Preview of point deformation on a multibody part - three bodies selected
|
|
|
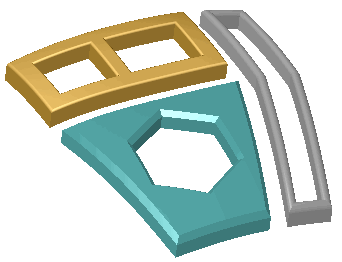
Result of point deformation on a multibody part
|
|
Deform - Curve to Curve
Curve to curve deform is a more precise method for altering complex shapes. You deform objects by mapping geometry from initial curves, which can be sets of curves, edges, section curves, sketch curves, and so on, to a set of target curves.
 curve to curve deformation of a knife handle
curve to curve deformation of a knife handle
 curve to curve deformation of a piston using tangency matching
curve to curve deformation of a piston using tangency matching
Options for controlling deform shapes let you:
-
Fix edges and faces so they cannot move.
-
Add additional faces or bodies to deform.
-
Set stiffness and shape accuracy.
If the target curve is a face or surface edge, you can match the deform model's initial edges using position continuity
(a sharp transition) or tangency
(smooth transition).
See Deform - Curve to Curve Options for details on the PropertyManager options. For additional examples of deforming models with the curve to curve option, see Deform - Curve to Curve Examples.
|
|
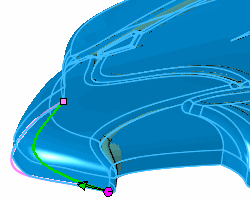
Target curve and body to deform
|
|
|
Curve to curve deform in process
|
|
|
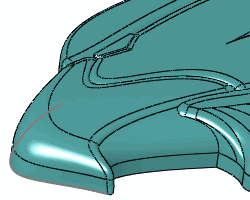
Curve to curve result
|
Deform - Surface Push
Surface push deform modifies surfaces of target bodies by displacing (pushing) them with tool body surfaces. The target body surfaces approximate the tool body surfaces while maintaining a one-to-one correspondence between every target surface before and after the deformation.
 surface push deformation of a car's dashboard
surface push deformation of a car's dashboard
Surface push deform provides more efficient control of the deform shape as compared to point deform. It is also a predictable way to create specific features based on tool body shapes. You can set exact coordinates to place the tool bodies, or you can dynamically move them with a triad  in the graphics area. You select a push direction for the tool body, target bodies to deform, a tool body or bodies, and a deform deviation value (similar to a fillet) to define the deform shape where the target and tool bodies intersect.
in the graphics area. You select a push direction for the tool body, target bodies to deform, a tool body or bodies, and a deform deviation value (similar to a fillet) to define the deform shape where the target and tool bodies intersect.
Use surface push deform to design free-form surfaces, tooling, plastics, soft packaging, sheet metal, and other applications where it is useful to incorporate the characteristics of tool bodies into existing designs.
 To make precise changes to models using a tool body method, see the
Indent
To make precise changes to models using a tool body method, see the
Indent
 tool, which creates exact offsets with user-specified clearance and thickness.
tool, which creates exact offsets with user-specified clearance and thickness.
See Deform - Surface Push Options for details on the PropertyManager options. For additional examples of deforming models with the surface push option, see Deform - Surface Push Examples.
|
|
|
|
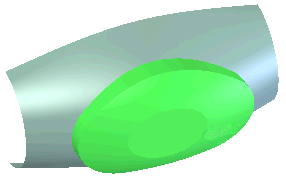
Surface push - tool body (green) and deform target
|
Surface push results
|