Analysis Procedure - Modal Time History
The system of equations of motion of a linear n-degree-of-freedom system excited by a time varying force is:
 (Equation 1)
(Equation 1)
where:
[M] = n x n symmetric inertia matrix
[C] = n x n symmetric damping matrix
[K] = n x n symmetric stiffness matrix
{f(t)} = n-dimensional force vector
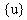 ,
,  ,
,  are the displacement, velocity, and acceleration n-dimensional vectors, respectively.
are the displacement, velocity, and acceleration n-dimensional vectors, respectively.
(Equation 1) is a system of n simultaneous ordinary differential equations with constant coefficients. The equations of motion are coupled through the mass, stiffness, and damping terms. Coupling depends on the coordinate system used to describe the equations of motion mathematically.
The basic idea behind modal analysis is to transform the coupled system of (Equation 1) into a set of independent equations by using the modal matrix [F
] as a transformation matrix. [
F
] contains the normal modes {
f
}
i for i = 1, ....,n arranged as:
 (Equation 2)
(Equation 2)
The normal modes and eigenvalues of the system are derived from the solution of the eigenvalue problem:
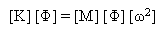 (Equation 3)
(Equation 3)
where [w2] is a diagonal matrix of the natural frequencies squared.
For linear systems, the system of n equations of motion can be de-coupled into n single-degree-of-freedom equations in terms of the modal displacement vector {x}:
 (Equation 4)
(Equation 4)
Substituting vector {u} from (Eq.4) and pre-multiplying it by [F]T (Equation 1) yields:
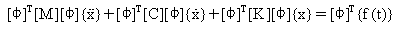 (Equation 5)
(Equation 5)
The normal modes satisfy the orthogonality property, and the modal matrix [F] is normalized to satisfy the following equations:
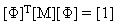 (Equation 6)
(Equation 6)
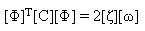 (Equation 7), and
(Equation 7), and
 (Equation 8).
(Equation 8).
By substituting (Equations.6--8), (Equation 5) becomes a system of n independent SDOF second-order differential equations:
 for i =1, ..., n (Equation 9)
for i =1, ..., n (Equation 9)
(Equation 9) is solved by using step-by-step integration methods like Wilson-Theta, and Newmark.
The integration is performed in the time domain, where the results of the last step are used to predict those of the next one.
The system's displacement vector (u) is derived from (Equation 4).
Related Topics
Solution Accuracy for Dynamic Analysis
Damping Effects