The excitation at two nodes can be fully correlated, fully uncorrelated, or partially correlated.
Partial correlation is based on the spatial distance Rij between two nodes. Depending on the relation between user defined parameters RMIN, RMAX and Rij:
| Fully correlated |
Distance Rij is smaller than the user defined RMIN ( Rij < RMIN). |
| Fully uncorrelated |
Distance Rij is larger than the user defined RMAX ( Rij > RMAX). |
| Partially correlated |
Distance Rij is between the user defined RMIN and RMAX ( RMIN < Rij < RMAX). The degree of correlation is constant for RMIN less or equal to Rij and decreases linearly for the interval RMAX - RMIN. |
The above conditions are illustrated in the figure.
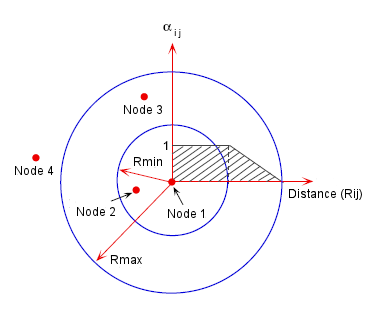
In the figure above:
- Nodes 1 and 2 are fully correlated.
- Nodes 1 and 4 are fully uncorrelated.
- Nodes 1 and 3 are partially correlated.
The effect of the node distance on the cross-correlation terms (off-diagonal terms) of the section of the PSD excitation matrix that is related to two nodes (i) and (j) is written as:
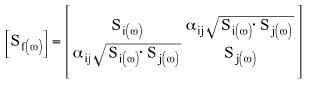 (Eq.1)
(Eq.1)
where:
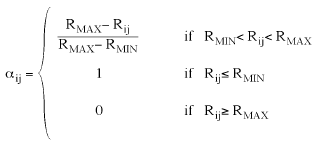
(Eq.2)