Conduction is the heat transfer mechanism in which thermal energy transfers from one point to another through the interaction between the atoms or molecules of the matter. Conduction occurs in solids, liquids, and gasses.
Conduction does not involve any bulk motion of matter. Gases transfer heat by direct collisions between energetic molecules, and their thermal conductivity is low compared to solids since they are dilute media. The conduction of energy in liquids is the same as in gases except that the situation is considerably more complex since the molecules are more closely spaced and molecular force fields exert a strong influence on the energy exchange in the collision process. Nonmetallic solids transfer heat by lattice vibrations so there is no motion of the media as heat propagates through. Metals are better conductors than nonmetals at normal temperatures because they have free electrons that carry thermal energy.
The heat transfer by conduction obeys Fourier's law which states that the rate of heat conduction Qconduction is proportional to the heat transfer area (A) and the temperature gradient (dT/dx), or:
Qconduction = - K A (dT/dx)
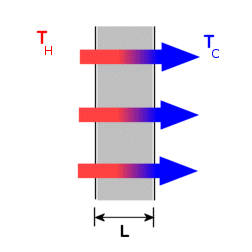
where K, the thermal conductivity, measures the ability of a material to conduct heat. The units of K are W/m.ºC or (Btu/s)/in.ºF. For the planar layer shown below, the rate of heat conduction is given by,
Qconduction = - K A ( TH - TC )/L
The figure below shows range values for the thermal conductivity for liquids, nonmetallic solids, and pure metals at normal temperature and pressure.

Temperature Dependence of the Thermal Conductivity (K)
For most materials, K varies with temperature. It rises with temperature in gases at low pressures, but it may rise or fall in metals or liquids.
The following table lists thermal conductivities (in W/m.ºK) versus temperature (in ºK) for selected materials:
| Metal |
Temperature (ºK) |
| 103 |
173 |
273 |
373 |
473 |
573 |
673 |
873 |
| StainlessSteel |
|
|
|
15 |
17 |
19 |
21 |
25 |
| Lead |
40 |
37 |
36 |
34 |
33 |
32 |
17 (liq.) |
20 (liq.) |
| Platinum |
78 |
73 |
72 |
72 |
72 |
73 |
74 |
77 |
| Zinc |
124 |
122 |
122 |
117 |
110 |
106 |
100 |
60 (liq.) |
| Silicon |
856 |
342 |
168 |
112 |
82 |
66 |
54 |
38 |