The friction factor is also known as torque coefficient.
The definition of friction factor is given in: Mechanical Engineering Design 5th edition by Shigley and Mischke, Chapter 8-8, pages 345 - 347.
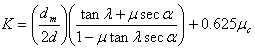
d = major diameter of the screw
dm = mean diameter of the screw
λ = lead angle of the thread; tan λ = p/π dm (where p is the pitch)
2α = thread angle (2α = 29° for Acme threads and 2α = 60° for ISO metric M threads)
μ = friction coefficient for the threads
μc = coefficient of collar friction for the screw head
The coefficients of friction μ and μc depend upon the surface smoothness and the degree of lubrication. Average values for μ and μc are approximately 0.15.
The following table includes typical values for the friction factor
(Bowman Distribution-Barnes Group, Fastener Facts, Cleveland, 1985, page 90). If the bolt condition is unknown, K = 0.20 is recommended.
| Bolt condition |
K |
|---|
| Nonplated, black finish |
0.30 |
| Zinc-plated |
0.20 |
| Lubricated |
0.18 |
| Cadmium-plated
|
0.16 |
| With Bowman Anti-Seize |
0.12 |
| With Bowman-Grip nuts |
0.09 |