Mesh quality plays a key role in the accuracy of the results. The software uses
two important checks to measure the quality of elements in a mesh.
Aspect Ratio Check
For a solid mesh, you achieve the best numerical accuracy with a mesh that has
uniform perfect tetrahedral elements whose edges are equal in length. For a general
geometry, you cannot create a mesh of perfect tetrahedral elements.
Because of small edges, curved geometry, thin features, and sharp corners,
some of the generated elements can have much longer edges than others. When the
edges of an element differ in length substantially, the results are less
accurate.
The aspect ratio of a perfect tetrahedral element is used as the basis for
calculating aspect ratios of other elements. The aspect ratio of an element is the
ratio between the longest edge and the shortest normal dropped from a vertex to the
opposite face, normalized with respect to a perfect tetrahedral.
By definition, the aspect ratio of a perfect tetrahedral element is
1.0. The aspect ratio check assumes straight edges connecting the four corner nodes.
The software calculates the aspect ratio to check the mesh quality.
Example
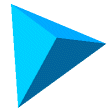 |
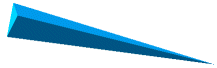 |
| Element with aspect ratio
close to 1.0 |
Element with large aspect
ratio |
Jacobian Ratio Check
Available for second order mesh elements (high quality solid and
shell
mesh).
The Jacobian ratio measures the deviation of an element’s shape from
an ideally shaped element (one that has straight edges with equal
lengths).
The Jacobian ratio of a perfect second order tetrahedral element with linear edges
is 1.0. The Jacobian ratio of an element increases as the curvature of the element
edges increases to map a curved geometry.
Near extremely sharp or curved boundaries, the edges of an element
can cross over each other
and the element becomes
distorted,
resulting in self-intersecting geometry. Distorted elements have a negative Jacobian
ratio and produce inaccurate
results.
In the Mesh PropertyManager, the
Issue warning for distorted elements option alerts
you if there are distorted elements in the mesh. To remove
distorted elements, first check the model for any geometry irregularities. Refine
the mesh in areas where distorted elements exist.
The Jacobian ratio check considers the Gaussian points located within
each element. The default value in a new study is 16 Gaussian points.
Recommendation: Set Jacobian
check to At Nodes when using
the p-method to solve static
problems.
For high-order shells, the Jacobian
check uses 6 points located at the nodes.
A
good
quality mesh has a Jacobian ratio
between 1 and 10 for the majority of its elements (90% and above). Create a Mesh
Quality Plot to plot the Jacobian ratio.