The Fill Settings define the injection molding process parameters such as
Filling Time, Melt
Temperature
Mold Temperature, and Injection Pressure Limit.
To open the Fill
Settings PropertyManager:
- In the PlasticsManager, expand Process Parameters, and click Fill
Settings.
Process Parameters
|
Filling Time
|
Specifies the time it takes the molten plastic to fully
fill the cavity. The program calculates
automatically the Filling
Time based on the part geometry and the
properties of the material you select.
Click Auto
 to enable
editing of the Filling
Time. to enable
editing of the Filling
Time.
If you use the
Advanced options
below to control the filling process, the software recalculates
the Filling
Time.
The diagram shows the
variation of injection pressure (y-axis) with respect to filling
time (x-axis). The U-shape diagram indicates that the optimal
filling time is located at the bottom of the curve. For short or
very long filling times, higher injection pressure values are
required. 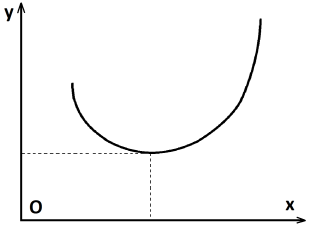
|
| Melt
Temperature(oC) |
Specifies the temperature of the polymer at the
injection location (or locations). The default
value for Melt
Temperature is taken from the material database
(see Polymer-Material
Parameters tab of the selected material).
Click Reset
 to reset the
Melt Temperature to
its default value. to reset the
Melt Temperature to
its default value.
|
|
Mold Temperature(oC) |
Specifies the temperature that the mold is heated to. The default value for Mold Temperature is taken from
the material database.
Click Reset
 to reset the
Mold Temperature to
its default value. to reset the
Mold Temperature to
its default value.
If the
mold temperature is not constant but varies with time,
select Mold Temperature
profile to enter the mold temperature
data.
|
| Injection Pressure Limit |
Specifies the maximum allowed value of the pressure of
the polymer at the injection location (or locations). If the pressure reaches the Injection Pressure Limit value,
the inlet flow rate automatically reduces to a value
corresponding to this limit, and the Filling Time is longer than the
Filling Time value that is set.
You can adjust the default Injection Pressure Limit
according to the capacity of your machine.
Click Reset
 to reset the
Injection Pressure
Limit to its default value. to reset the
Injection Pressure
Limit to its default value.
|
| Clamp
Force Limit |
Specifies the maximum allowed value of the force required to keep the
mold closed. If the force reaches the Clamp Force Limit value, a
warning alerts you in the Analysis Manager, and the analysis
continues unimpeded.
You can adjust the default Clamp Force Limit according to
the capacity of your machine.
|
Advanced
| |
Flow/Pack Switch
Point
(% Filled
Volume)
|
Controls the process changes from FLOW to PACK. During FLOW, polymer is forced into
the cavity at a given flow rate, regardless of pressure. To
avoid a rapid pressure rise and potential damage to the machine,
it is common to switch from FLOW to PACK just before the cavity
becomes full, for example at 95% of the cavity
volume.
|
| |
Temperature Criteria for Short Shots(oC) |
If the temperature in the molten polymer is
below this temperature value, a warning alerts you in the
AnalysisManager.
If the temperature stays below this value for
several iteration steps, a short-shot occurs. The polymer
solidifies and the melt flow stops.
|
| |
Multi general Gate Flow-rate/Press
control
|
Available for shell
analysis
procedure only and multiple injection locations.
|
Equivalent
|
Distributes equal flow rates at each
injection location, with potentially different resulting
pressures.
|
|
Automatic
|
Balances the flow between injection
locations to produce equal pressures, simulating the
effect of a runner system.
|
|
| |
Gravity Direction: (Global) |
Defines the direction of gravity. For example, if the model is oriented in the injection molding
machine such that the positive Y- axis points upward, select the
negative Y- axis for the gravity
direction.
Gravity Direction is
available for the solid analysis procedure.
|
 |
Flow Rate Profile Settings
|
Controls the flow rate during the
filling of the cavity by defining a Flow
Rate Profile based either on volume or time
control. |
| |
Volume control (Absolute control)/Base on machine max flow
rate |
You can control the variation of
Flow rate or Screw speed in terms of the
percentage of filled cavity volume, or the screw position. By
default you can enter five data pairs. You can increase the number
of data pairs in Section num.
|
Flow rate (cc/sec) or (in3/sec)
|
Specifies the volumetric flow rate.
|
|
Flow rate (%)
|
Specifies the flow rate as a percentage
of the Reference flow
rate. For example, if the Reference flow rate
(cc/sec) is 350, and you enter a
flow
rate of 80%, then the actual flow rate is 280 cc /
sec.
|
|
Screw speed
|
Used together with the Screw diameter to
calculate the flow rate (flow rate = Screw speed * Screw
section Area).
|
|
Screw position
|
Used together with the Initial screw position
to define the volume of material delivered to the
cavity.
|
|
Volume (%)
|
The percentage of the filled cavity
volume.
Enter
a value of 100% in the last table entry.
|
- Specify an Initial screw
position, if the Flow
Rate depends on the screw position.
- Specify a Reference flow rate (cc/s), if you
define the flow rate as a percentage of the reference
flow rate.
- Specify a Screw diameter, if the flow rate
depends on the screw speed.
|
| |
Time
control (Relative control)/Base on filling
time |
Specifies
the profile of a relative flow rate versus the filling time or a
percentage of the total filling time.
|
Filling Time (sec)
|
Displays the filling time from the
Fill
Settings PropertyManager. You can enter
the filling time profile data in absolute (Time sec) or relative
values (Time
%).
|
|
Flow rate (%)
|
The Flow
Rate (%) values you enter in the table
are interpreted relative to each other. For example, if
two data points are defined with Flow Rate values of 10%
and 30%, the flow rate for the second data point
is
three times larger than the first flow rate value.
The
software calculates the actual
volumetric flow rates for each data point to satisfy the
given relative profile and the filling time for the
cavity.
|
|
| |
Apply |
Applies the current settings to the current of
the flow rate profile.
|
 |
Machine Database
|
From the injection molding machine database, select an
injection machine. The injection molding machine database is
provided as a reference only. The selection of any machine does
not have any effect on the analysis settings or results. If you
want to use any data from the machine database, enter the data
into the Analysis Process parameters.
When you select a machine from the database, you
need to copy the selected machine's parameters in the respective
Fill Settings
PropertyManager input fields. The software does not transfer the
selected machine's default values for Injection Pressure Limit,
Screw Diameter
(Flow Rate Profile
Settings dialog box), and Reference Injection Rate
(Flow Rate Profile
Settings dialog box)
automatically.
|
| |
Viscoelastic Birefringence Calculation
|
Activates the Birefringence
calculation.
Select
a polymer
that
includes definitions for the Birefringence material parameters to
use this feature.
These material parameters are the Leonov
parameters in the Material Database / Polymer-Material
Parameters.
|
Solver Settings
|
Options
|
Provides access to the advanced solver settings.
Accept the default values of the solver settings to produce the best
results over a wide range of cases. For most analyses, you do not
need to modify the solver settings. See topic Advanced
Settings for the Flow/Pack Solver.
|
Fiber Orientation Calculation
To improve the strength and performance of plastic products, many
plastics contain fibers. The fiber percentage of each material is included in the
polymer material database. Material data, such as viscosity coefficients, reflect
the properties of a particular fiber % and polymer combination.
During cavity filling, the fibers become oriented along the flow
directions. This produces changes in the microstructure that affect the mechanical
properties and final dimensions of the product.
For polymer materials that have a % fiber value, select Fiber Orientation Calculation to compute fiber
orientations during the simulation.
|
Current % Fiber based on
Weight
|
Specifies
the percentage of fiber in the material based on weight. For example: for 1 kg material with 200 gr of
fiber, you enter 20 (%) for Current
% Fiber based on Weight;
If
you select a polymer from the Material Database, the fiber
percentage value is taken from the
database.
|
Co-injection
In a co-injection simulation, the machine injects two polymers (or a
polymer and a gas) sequentially into the cavity. Typically, the first material
becomes skin and the second material fills the core. Co-injection is also used for
Gas Assist injection molding,
where you
select a gas for the second
material,
and the part becomes hollow.
In the material dialog box,
select , and select the second material from the plastics database.
|
2nd Material Melt
Temperature
|
The default value is taken from the material
database (see Polymer-Material
Parameters tab of the selected material data
sheet).
|
Venting Analysis
In general, the presence of air in the cavity is ignored during simulation.
However, venting analysis allows you to include the effect of the air, and the
pressure that it may exert on the melt front.
If you run venting analysis, you must define vent locations in the
cavity (see ). Venting analysis identifies and tracks bubbles that may form and
coalesce in the cavity away from air vents and computes the pressure that develops
in them.
For the first analysis, it is recommended to not define any air vents. Use the
Venting Pressure result to guide air vent placement, and
avoid placing them where they are not required.
| Cavity Initial Air Pressure (MPa)
|
The initial air pressure when the cavity is empty is
14.71 psi or 0.1 MPa by default. |
| Cavity Initial Air Temperature () |
The initial air temperature in
the cavity is the room temperature by default. |
Mold-Melt Heat Transfer Coefficient
The heat transfer between the polymer and the mold walls varies
during the different stages of the injection process:
- During the filling stage, the polymer enters the cavity,
and the heat transfer raises to the maximum value.
- During the packing stage, the polymer is in contact with
the mold walls, and the heat transfer stays at the maximum value.
- During the ejection stage, the polymer shrinks during the
pre- cooling time, and detaches partially from the mold walls. The heat
transfer is reduced in this stage.
Reactive Control Type
Available only when you select a thermoset polymer material. Examples of
thermoset material families available in the Plastics database include: BMC, EMC,
and LSR.
In thermoset injection molding, the plastic in a liquid state (typically at room
temperature or colder) is injected into a heated mold. The heat from the mold
induces a chemical reaction that creates cross-links (permanent connections between
molecular chains) in a process known as curing. Choose between two different options
to determine the duration of the analysis.
| Conversion |
When selected, the Fill/Pack stage lasts until
the analysis reaches the specified value for the Reactive Eject Conversion:
(%).
|
| Time |
When selected, you explicitly define the
duration of the Fill and Pack phases. At the end of the analysis,
you can review the curing conversion % to better understand whether
your specification is appropriate. |
| Reactive Eject
Conversion: (%) |
Specifies the required conversion degree.
Available when you select Conversion. |
Mold Temperature Profile
If the mold temperature is not constant but varies with time,
select Mold Temperature profile.
Enter the mold temperature variation in terms of absolute time or as
a percentage of the total process time. The total process time includes Fill, Pack,
and Cool time.
For a more detailed consideration of mold temperature, you can perform a
Cool simulation, where heat transfer
between the cavity, mold, and cooling channels is computed. These results provide
temperatures that vary both in location and in time. These Cool
simulation results override any values you enter for Mold Temperature and Mold Temperature
Profile.
 |
Edit/Show Profile
|
Select to
define
the mold temperature profile during the injection process. Enter the
values of mold temperature versus time (in seconds or in percentage
values of the total process time). |