| Polymer |
Melt
Temperature |
Defines
the
material manufacturer’s
recommended
temperature of the polymer as it exits the molding
machine through the nozzle and enters the mold. Minimum and
maximum
values define
the
manufacturer’s allowable range. |
| Polymer |
Mold
Temperature |
Defines
the
material manufacturer’s recommended temperature of the mold during
injection. Minimum and maximum values define the manufacturer’s
allowable range. |
| Polymer |
Ejection
Temperature |
Defines the temperature of the part when it has cooled down and is
ready for ejection. |
| Polymer |
Transition
Temperature |
Defines the temperature at which a polymer changes
from melted to solid state. For semicrystalline materials, this is a
precise temperature. For amorphous materials, the transition occurs
gradually over a range of temperatures, but is given as a single
value. |
| Polymer, and
Coolant |
Viscosity |
Defines a measure of a melted
polymer's
resistance to a flow. Highly viscous fluids, like peanut butter, resist
a flow much more than low viscosity fluids like water. Most polymers are
non-Newtonian, which means their viscosity is dependent on the shear
rate they experience.
Polymers
solidify as they cool, so their viscosity also depends on
temperature. |
| Polymer, and
Coolant |
PVT(pressure,
volume, temperature) |
Defines the relationship between pressure, volume,
and temperature parameters that evaluate how much a polymer
shrinks
as it cools from melted to solid state during the
injection molding process. |
| Polymer, and
Mold |
Solid
Density |
Defines the
mass-per-unit
volume of a material in its solid state. |
| Polymer,
Mold,
and Coolant. |
Specific
Heat |
Defines the amount of energy required to heat one
kilogram of a material by one Kelvin. |
| Polymer,
Mold,
and Coolant |
Thermal
Conductivity |
Defines a measure of how easily thermal energy can
transfer through a material. |
| Polymer,
Mold |
Elastic
Modulus |
Defines a
measure
of a
material's resistance to deform elastically under
stress application. More specifically, the ratio of tensile stress to
tensile strain (also known as Young's modulus). |
| Polymer,
Mold |
Poisson's
ratio |
Defines the ratio of transverse contraction strain to
longitudinal
extension
strain in the direction of
the
stretching force. |
| Polymer,
Mold |
Thermal Expansion
Coefficient |
Defines a measure of how a material expands and
contracts because of changes in temperature. |
| Polymer |
Shear Relaxation
Modulus |
Defines a measure of how a material relieves stress
over time when subjected to constant strain. |
| Polymer |
Curing
Model |
Describes the curing process for a thermoset
material. |
| Polymer |
No-Flow
Temperature |
Defines the temperature at which a polymer no longer
flows. |
| Polymer |
Melt Flow
Rate |
Defines a measure of the ease of flow of a melted
polymer. |
| Polymer |
%
Fiber |
Defines the percentage of fiber filler by
weight. |
| Polymer |
Max Shear
Rate |
Defines the material manufacturer’s maximum allowable
shear rate. |
| Polymer |
Max Shear
Stress |
Defines
the material
manufacturer’s maximum
allowable
shear stress. |
| Polymer |
Stress Optical
Coefficient |
Defines a measure of the amount of
birefringence
because of residual stress in a transparent polymer. Birefringence is
the optical property of a material having a refractive index that
depends on the polarization and propagation direction of
light.
|
| Polymer |
Leonov
Parameters |
Defines the parameters of the Leonov Viscoelastic
Model used to predict birefringence. Viscoelastic materials exhibit both
viscous and elastic behavior under stress. Material deformation is
temporary
when
the
stress is removed quickly,
but permanent when the stress is sustained. |
| Polymer |
WLF
Parameters |
Defines the Willams-Landel-Ferry (WLF)) equation
coefficients for the Leonov Viscoelastic Model. The WLF equation
is: 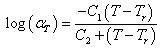 where T is the temperature, Tris a reference
temperature, and C1 and C2 are empirical
constants.
|
| Polymer, and
Mold |
Parallel Shear
Modulus |
Defines the in-plane ratio of shear stress to shear
strain. |
| Polymer |
Crystallization
Kinetics |
Defines a measure of the crystallization process of a
semicrystalline polymer that occurs between its melting point and
glass transition temperature.
|
| Polymer |
Juncture Loss
Coefficients |
Defines a measure of the hydraulic loss experienced
when a polymer flows through a significant change in cross-sectional
area, such as those common to a runner system. |
| Polymer |
Data
Source |
Defines the source of the data. |