| Method |
Sets the method of integration.
|
Standard
|
It takes more time but generates more
accurate results (recommended).
|
|
Approximate
|
|
|
| Gauss
integration order |
Gauss integration order to be used
in integration of response power spectral densities. The options are
two-point and three-point Gaussian integration. |
| Biasing
parameter |
Sets the value of biasing
parameter, which controls the selection of frequency points for
integration. The power spectral density (psd) of the response is
evaluated at these frequency points. See
topics Methods of Integration and
Selection of Frequency Points
for more information.
|
| Cross-mode cut-off ratio |
Sets the cut-off ratio of any two natural
frequencies above which the cross-mode effects are neglected.
For example, if you set this ratio to 5, cross
correlation effects are neglected between modes i and j
(i>j), if wj / wi is larger than 5.
|
| Include
extra frequencies for response |
Select this option to include extra frequencies
of interest for the calculation of the response parameters to
random vibration loads.
In addition to the natural frequencies, which are
included in the random vibration analysis by default, you can
select up to 20 extra frequency points of interest. Enter the
extra frequency points in ascending order (positive values).
The number of solution frequency points at which
the solver calculates the response (that is, the clustered
frequency solution points between two consecutive frequencies)
is identical to the number of frequency points used for the
natural frequencies (see No. of
points for each frequency).
|
| Edit |
Select this option to enter up to
20 frequencies in ascending order (positive values). |
| Tolerance to merge extra frequency points |
Sets a tolerance limit (%) that defines how close
an extra frequency point is to a natural frequency or to its
consecutive extra frequency point so that the solver can merge
the two consecutive frequencies into one frequency. The default
tolerance limit is 1%. The solver does not
apply the tolerance criterion to natural frequency points
(that is, natural frequencies are not merged).
|
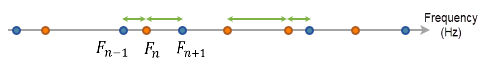
 represents natural frequencies calculated by
the solver (all natural frequencies are included in the
calculation of RMS output). represents natural frequencies calculated by
the solver (all natural frequencies are included in the
calculation of RMS output).
 represents user-defined extra frequency points
to include in the calculation of RMS output. represents user-defined extra frequency points
to include in the calculation of RMS output.
 represents tolerance (%). represents tolerance (%).
For example, the solver merges an extra frequency
point to its closest natural frequency, based on the following
criteria:
|