Description
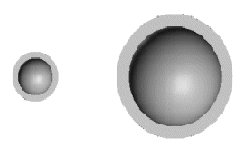
The thermal energy exchange through radiation between two spherical faces is compared with theoretical results. The two spheres are hollow with fixed temperatures at the inner faces. The two faces are assumed to radiate as black bodies (emissivity = 1.0). Radiation to the atmosphere is not considered (closed system).
File Name
Browse to
drive letter:\Users\Public\Public
Documents\SOLIDWORKS\SOLIDWORKS version\samples\Simulation
Examples\Verification\Thermal_11.SLDASM and open the
file.
Study Type
Steady state thermal analysis.
Meshing Parameters
Default element size and tolerance. Identical local mesh controls are defined on the outer faces of the two spheres.
Results
- The theory calculates the Radiation View Factor (RVF) of each sphere to the
other. The RVF from the smaller sphere to the larger one is calculated as
0.0459. The theoretical thermal energy (E) received by the colder sphere,
which is equal to the thermal energy radiated by the hotter sphere, is
calculated from:
E = Stefan-Boltzman constant * RFV*
Emissivity * Area of small sphere * (T4smallsphere -T4largesphere) = 5203.9 Watts
- Use the List Heat Power tool to list the
resultant heat flux on each of the outer faces of the two spheres. The two
values should be equal in magnitude but opposite in sign.
| |
Analytical Solution |
SOLIDWORKS Simulation |
| Thermal
heat exchange at steady state (Watts) |
5203.9 Watts |
For the large sphere = +5161.7 Watts
For the small sphere = -5161.7 Watts
|