Description
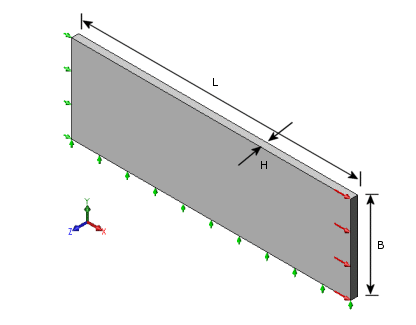
A bar made of a viscoelastic material is fixed at one end and a constant axial pressure is suddenly applied at the other end. Compare the axial strain to analytical results. The bar dimensions are as follows: L = 10", B = 3.14159", H = 0.25".
File Name
Browse to drive
letter:\Users\Public\Public Documents\SOLIDWORKS\SOLIDWORKS
version\samples\Simulation
Examples\Verification\Nonlinear_Static_10.SLDPRT and open the
file.
Shell Parameters
Shell thickness = 0.25" - thick shell formulation.
Meshing Options
Draft, Standard, 4 Points, and Smooth surface.
Meshing Parameters
Use a Global Size of 0.5".
Material Model
Viscoelastic material model.
Material Properties
Modulus of elasticity = 10,000 psi, (NUXY)o = 0.4833, Shear relaxation modulus = 0.9010, Time value for the shear relaxation modulus = 0.9899 sec.
Restraints and Loads
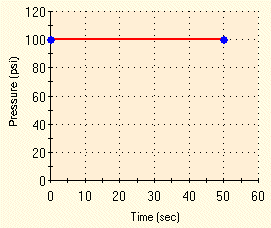
Restraints are illustrated on the figure above. The pressure is applied suddenly as follows:
Results
The following
table
summarizes the results for the instantaneous and long term behaviors:
| |
Instantaneous Behavior (t = 0.001
sec) |
Long Term Behavior (t = 50 sec)
|
| Theory
|
(NUXY)o
= 0.4833 |
(NUXY)∞
= 0.4983 |
| SOLIDWORKS Simulation (average values) |
(NUXY)o
= - EPSY/EPSX = 0.4833 |
(NUXY)∞
= - EPSY/EPSX = 0.4974 |
The time history of the axial strain from SOLIDWORKS Simulation is in
good agreement with the analytical solution:
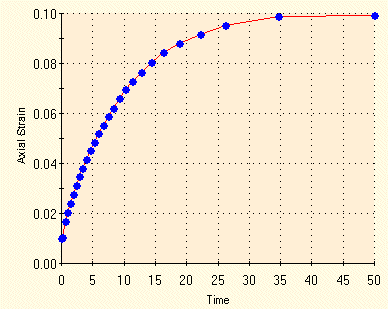
The above graph was not generated directly in SOLIDWORKS
Simulation. Results have been processed to generate the graph externally.
Reference
R. M. Christensen, “Theory of Viscoelasticity – an Introduction,” 2nd Ed., 1982, pp. 1-76.