The Add Event (Harmonic) PropertyManager defines a fatigue event that is based on stress results from a linear dynamic - harmonic study. You can predict the damage and remaining life of a part that is exposed to repeated cyclic loading at a given operating frequency.
Available for SOLIDWORKS Simulation Premium.
To open the Add Event (Harmonic) PropertyManager:
- Create a fatigue study based on a linear dynamic harmonic study. In the fatigue study tree, right-click Loading (Harmonic)
 and select Add Event.
and select Add Event.
Study
In a Constant amplitude fatigue event, the loading / unloading cycle is performed
slowly (semistatic). In a fatigue event based on a dynamic harmonic study, the
cyclic loading / unloading is performed at a given operating frequency. For a
harmonic excitation at higher frequencies, the inertia of the model plays an
important role in magnifying the cyclic excursion of the response.
 |
Study Association (Linear Dynamic -Harmonic Study)
|
Specifies the reference study. From the list of
available studies, select one linear dynamic harmonic study. Recommendation: Run the selected harmonic study
before you set up a fatigue event.
|
Plot Step
 |
Frequency
|
Specifies the frequency value of the sinusoidal fatigue
loading. Fatigue damage estimates are based on stress results at the
given frequency value. |
 |
Plot Step
|
Specifies the solution step number for the
corresponding frequency value. The nearest plot step is shown for
the selected frequency. |
Scale and Cycles
 |
Cycles
|
Specifies the number of cycles (an integer value)
associated with this event. |
 |
Scale Factor
|
Applies a scale factor to the stress results of the selected frequency. The program multiplies the stress results at the specified frequency by this factor to calculate the alternating stresses.
|
You can create multiple fatigue events that are based on the same linear dynamic
harmonic study. The software assumes that the events occur sequentially one
after the other without any interaction. The von Mises stress is used to
calculate the equivalent alternating stress for extracting the number of cycles
to failure from the S-N curve.
The calculation of the cumulative damage ratio is based on the
Linear Damage or Palmgren- Miner's rule:
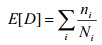
where E [D] is the expected damage ratio, nI
is the number of cycles the part is subjected at a certain operating frequency
and alternating stress SI and NI is the
number of cycles required to cause failure at stress level SI
given by the material's S-N curve.