Deform - Point Options
The Point deformation is based on a point and its pull direction vector. See Deform - Point Examples for more point deformation examples.
Deform Point
-
Deform Point  . To set the center of deformation, select a point on a face, an edge, a vertex, or a point in space.
. To set the center of deformation, select a point on a face, an edge, a vertex, or a point in space.
-
Deform direction. Choose a deform direction by selecting a linear edge, sketch line, planar face, plane, or two points or vertices.
-
-
If you select a linear edge or line, the direction is parallel to edge or line.
-
if you select a plane or planar face, the direction is normal to the plane or face
-
If you select two points or vertices, the direction follows the first to second point or vertex.
-
Any combination of deform points and directions may be used.
-
If necessary, click Reverse deform direction  .
.
When the deform point is on a face, edge, or vertex, the default direction is as follows:
 Example of point on face.
Example of point on face.
 Example of point on edge.
Example of point on edge.
 Example of point on vertex.
Example of point on vertex.
-
Point in space. When you select a point in space, there is no deform direction, so you must specify one by selecting two points or vertices, a linear edge or sketch line, or a planar face or plane. Point-in-space selection allows precise control of the point and deform direction and is useful when more control is needed for point deformations.
 Example of point in space.
Example of point in space.
-
Deform distance  . Specifies the distance of deformation (point displacement).
. Specifies the distance of deformation (point displacement).
-
Show preview. Previews results using wire frame (cleared) or shaded (selected) views. To improve performance with large and complex models, do not select this option until you have made all your selections.
Deform Region
This section allows you to alter the shape by specifying a radius of deformation, a deform region, and additional bodies to deform.
 You can use the options Fixed curves/edges/faces
You can use the options Fixed curves/edges/faces  , Bodies to be deformed
, Bodies to be deformed  , and Additional faces to be deformed
, and Additional faces to be deformed  in any combination, dependent on the geometry of the model and the desired results. If the selected options conflict, the last entity selected overrides any previous, contradictory selected entity. For example, if you first specified a face to deform and then specified the same face as fixed, the face would be fixed.
in any combination, dependent on the geometry of the model and the desired results. If the selected options conflict, the last entity selected overrides any previous, contradictory selected entity. For example, if you first specified a face to deform and then specified the same face as fixed, the face would be fixed.
Selecting Deform region does not affect the Deform radius value.
 of how Deform distance
of how Deform distance  and Deform radius
and Deform radius  affect the model with point deform
affect the model with point deform
 using a point on face with Deform region
using a point on face with Deform region
|
Selected entity for Deform Point
|
Deform region Option Status
|
Results
|
|
A point on an edge, vertex, or in space
|
Selected or cleared
|
Deformation area is not affected if Fixed curves/edges/faces  or Additional faces to be deformed or Additional faces to be deformed  are cleared are cleared
|
|
A point on a face
|
Selected
|
Deformation area is limited to that face if Fixed curves/edges/faces  or Additional faces to be deformed or Additional faces to be deformed  are cleared are cleared
|
|
A point on a face
|
Cleared
|
Whole body is deformed
|
-
Fixed curves/edges/faces  . Prevents the selected curves, edges, and faces from deforming and moving. With closed contours, deformation behavior depends on the following:
. Prevents the selected curves, edges, and faces from deforming and moving. With closed contours, deformation behavior depends on the following:
-
-
If the deform point (center of the deformation) is within the closed contour (contiguous set of fixed edges), the deformation is confined to the area within the contour.
-
If the deform point is outside the closed contour, no point inside the contour area is deformed.
 using Fixed curves/edges/faces
using Fixed curves/edges/faces 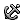
 deform point inside and outside of a closed contour.
deform point inside and outside of a closed contour.
 of selecting Additional faces to be deformed
of selecting Additional faces to be deformed 
 example of multibody deformation. There are four initial bodies to deform. One body is selected with a point in space. Then four bodies are selected to deform.
example of multibody deformation. There are four initial bodies to deform. One body is selected with a point in space. Then four bodies are selected to deform.
Shape Options
You control the shape of point deformations by modifying the degree of Stiffness, specifying a Deform axis
 , and modifying the Shape accuracy
, and modifying the Shape accuracy
 .
.
-
Deform axis  (available when Deform region is cleared). Controls the shape of the deformation by creating a bending axis parallel to a linear edge or sketch line, normal to a plane or planar face, or following two points or vertices. This option creates a bending-type deformation using the Deform radius
(available when Deform region is cleared). Controls the shape of the deformation by creating a bending axis parallel to a linear edge or sketch line, normal to a plane or planar face, or following two points or vertices. This option creates a bending-type deformation using the Deform radius  value, although not an exact bending. For exact bending, see the
flex feature
.
value, although not an exact bending. For exact bending, see the
flex feature
.
 of deform axis
of deform axis
You control the shape of point deformations by modifying the degree of Stiffness, specifying a Deform axis
 , and modifying the Shape accuracy
, and modifying the Shape accuracy  .
.
 of shape stiffness levels
of shape stiffness levels
-
Shape accuracy  . Controls the surface quality. The default quality can be inadequate in high curvature areas. When you increase the accuracy by moving the slider to the right, you can increase the success rate of the deform feature. Move the slider only as needed because increasing surface accuracy decreases performance.
. Controls the surface quality. The default quality can be inadequate in high curvature areas. When you increase the accuracy by moving the slider to the right, you can increase the success rate of the deform feature. Move the slider only as needed because increasing surface accuracy decreases performance.
 Point deformation that affects a small area may not display if you are using the default image quality settings. To increase the quality, click Tools, Options, Document Properties,
Image Quality
. Move the Shaded and draft quality HLR/HLV resolution slider to the right, or select Optimize edge length.
Point deformation that affects a small area may not display if you are using the default image quality settings. To increase the quality, click Tools, Options, Document Properties,
Image Quality
. Move the Shaded and draft quality HLR/HLV resolution slider to the right, or select Optimize edge length.
-
Maintain boundary (available when Deform region is selected). Ensures that boundaries selected for Fixed curves/edges/faces 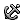 are fixed. Clear Maintain boundary to change the deform region, modify fixed edges, or allow the boundaries to move.
are fixed. Clear Maintain boundary to change the deform region, modify fixed edges, or allow the boundaries to move.
 of Additional faces only with Maintain boundary selected or cleared
of Additional faces only with Maintain boundary selected or cleared