If you apply initial conditions to a dynamic system, the system vibrates with decreasing amplitudes until it comes to rest. This phenomenon is called damping. Damping is a complex phenomenon that dissipates energy by many mechanisms like internal and external friction, thermal effects of cyclic elastic straining materials at the microscopic level, and air resistance.
It is difficult to describe dissipation mechanisms mathematically. Damping effects are usually represented by idealized mathematical formulations. For many cases, damping effects are adequately described by equivalent viscous dampers.
A viscous damper (or dashpot) generates a force that is proportional to velocity. A piston that can move freely inside a cylinder filled with a viscous fluid like oil is an example of a viscous damper. The damping force Fd is assumed to be linear with respect to the relative velocity at the two ends of the damper:
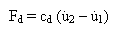 (Equation 1).
(Equation 1).
The constant cd, which is the slope of the curve Fd versus the relative velocity is called the coefficient of viscous damping;
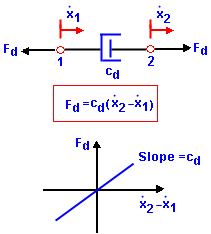
The units of coefficient of viscous damping are (force)/(velocity) or (force x time)/(length).
The response of a general viscously damped n-degree-of-freedom system is given by:
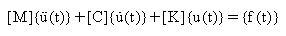 (Equation 2)
(Equation 2)
where:
[M] = n x n symmetric mass (or inertia) matrix
[C] = n x n symmetric damping matrix
[K] = n x n symmetric stiffness matrix
{f(t)} = n-dimensional force vector
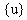 ,
, 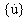 , and
, and 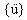 are the displacement, velocity, and acceleration n-dimensional vectors, respectively.
are the displacement, velocity, and acceleration n-dimensional vectors, respectively.
In general, classical modal analysis does not necessarily lead to an independent system of equations of motion unless the damping matrix [c] resulting from the modal coordinate transformation can be treated as a diagonal matrix.
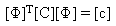 (Equation 3)
(Equation 3)
The following types of damping are available:
- Modal Damping
- Rayleigh Damping
- Composite Modal Damping
- Concentrated Dampers. Defined between two locations (available for modal time history analysis). See Spring-Damper Connector.