Composite modal damping allows the definition of the damping as a material property. Material damping ratio MDAMP is defined in the Properties tab of the Material dialog box. The program uses this property to calculate equivalent modal damping ratio for each mode.
The composite modal damping is defined in terms of equivalent modal damping ratios as:
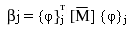
where:
βj = equivalent modal damping ratio of the jth mode
{φ}jT = jth normalized modal eigenvector
 = modified global mass matrix constructed from the product of the element's damping coefficient and its mass matrix.
= modified global mass matrix constructed from the product of the element's damping coefficient and its mass matrix.
If you specify material damping ratio MDAMP to be m for all materials in the model, the equivalent modal damping ratio will be m for all modes.