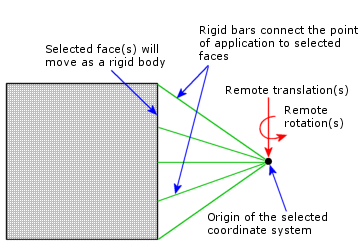
You can use this option when the replaced components are adequately rigid with respect to the modeled components and you know the remote translations and/or rotations that can replace its effect on the rest of the model.
The point of application of the constraint is effectively connected to the selected faces by rigid bars.
The selected face(s), being rigidly connected to a common point, can only deform as a rigid body. The area and shape of each face remain unchanged. High stresses can develop near faces with rigid connections.