Description
An aluminum
cylindrical bar
traveling
at a velocity of 478 m/s along its axial direction hits a rigid boundary. Calculate
the length of the bar at time t = 31 microseconds after initial
impact.
File Name
Browse to
drive letter:\Users\Public\Public
Documents\SOLIDWORKS\SOLIDWORKS
version\samples\Simulation
Examples\Verification\Aluminum_Bar.SLDPRT and open the
file.
Meshing Parameters
Use a Standard mesher with Global Size of 0.20 cm.
Material Properties
Elastic plastic with isotropic hardening:
- Elastic modulus = 70 GPa
- Poisson's ratio = 0.3
- Yield stress = 420 MPa
- Tangent Modulus = 0.1 GPa
- Density = 2700 kg/m3
- Hardening Factor = 0
Setup Parameters
- Initial velocity of bar = 478 m/s
- Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s2
The rigid target is oriented normal to the direction of gravity.
Results
The displacement UZ (cm) plot is shown at t = 31 microsec after the initial impact.
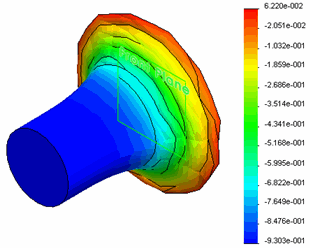
The maximum magnitude of UZ is about 0.93 cm at t = 31 microseconds. The length of the bar at this instant is (2.347-0.930=1.417 cm). Experimental results showed 1.319 cm.
Reference
Wilkins M.L. and Guinan M.W., "Impact of Cylinders on a Rigid Boundary", Journal of Applied Physics, Volume 44, No. 3, 1973.