Appearances Illumination PropertyManager
Use the Illumination  tab in the Appearances
PropertyManager to adjust
the lighting in part or assembly documents.
tab in the Appearances
PropertyManager to adjust
the lighting in part or assembly documents.
 If you have the PhotoWorks application add-in
selected, but cannot see the Illumination
If you have the PhotoWorks application add-in
selected, but cannot see the Illumination
 tab, click Advanced.
tab, click Advanced.
Illumination
Select an appearance type such as Satin
Finish to display its illumination properties.
Select or clear Dynamic help
to display pop-up tips for this PropertyManager. Pop-up tips include illumination
dependencies.
Select or clear Accurate reflections
(slower) to control the level of surface reflections.
To control illumination:
Move the slider or type a value between 0 and 1.
(Index
of refraction uses a different scale).

Caustics
Select or clear Cast. When selected, specular appearances
reflect caustic
photons. Light that hits either reflective or refractive objects
bounces, forming light patterns.
Select or clear Receive. When selected, diffuse appearances
absorb caustic photons. Light that hits either reflective or refractive
objects is absorbed.
 These options are available
only when Enable
Caustic on the Illumination
tab of the Options
dialog box is selected, and All appearances
cast and receive caustics by default is
cleared.
These options are available
only when Enable
Caustic on the Illumination
tab of the Options
dialog box is selected, and All appearances
cast and receive caustics by default is
cleared.
Global Illumination
Select or clear Cast. When selected, specular appearances
reflect photons. An object that is set to cast light reflects light and
indirectly illuminates an adjacent object.
Select or clear Receive. When selected, diffuse appearances
absorb photons. An object set receive light absorbs the light, causing
no effect on an adjacent object.
 These options are available
only when All appearances cast and receive
global illumination by default on the Illumination
tab of the Options
dialog box is cleared.
These options are available
only when All appearances cast and receive
global illumination by default on the Illumination
tab of the Options
dialog box is cleared.
Sampling rate
Controls the number of samples used to calculate the contribution of
the glossy component. Increasing the sampling rate reduces artifacts but
reduces performance. Available when the Material
Type is Satin Finish, Accurate reflections is selected, and
Glossy is non-zero.
Ambient
Controls the intensity of the light source. The level changes equally
on all sides of the model without attenuation or shadowing.
 The results vary widely. They depend on multiple
combinations, including the material, the color of the model, the degree
of ambience (intensity), as well as the color of the light. For example,
changing the color of the ambient light produces more noticeable results
with high ambience than with low ambience.
The results vary widely. They depend on multiple
combinations, including the material, the color of the model, the degree
of ambience (intensity), as well as the color of the light. For example,
changing the color of the ambient light produces more noticeable results
with high ambience than with low ambience.
Diffuse
Controls the intensity of the light on the surface. This property is
dependent on its angle to a light source but independent of the position
of the viewer.
 Increasing
the diffuse value makes the material appear brighter.
Increasing
the diffuse value makes the material appear brighter.
Glossy
Controls the specular factor of the lights reflected by the material.
Increasing the glossy value makes reflections more visible. Glossy reflections
are blurred and the amount of blur depends on Roughness.
Glossy also controls the intensity of the light on the surface, which
is dependent on the position of the light source and the position of the
viewer.
Specular
Controls the intensity of the light on the surface. This property is
dependent on the position of the light source and the position of the
viewer.
 Increasing the specular value makes the material
appear shinier.
Increasing the specular value makes the material
appear shinier.
Specular
Color. Controls the color of reflected highlights within the specular
component.
Specular spread
Controls the size of any highlights on a surface. Also known as specular
exponent, increasing the specular spread value makes highlights larger
and softer.
Specular Spread/Bluriness
Controls the size of any highlights on a surface and the bluriness of
reflections. Increasing the specular spread/bluriness value makes highlights
larger and softer and the reflections more blurry.
Reflectivity
Controls the reflectivity of a material. If the property is set to None, no reflections are visible on
a surface. If the property is set to Full,
the material simulates a perfect mirror.
Index of refraction
Controls the bending of light as it passes through a transparent object.
Although actually dependent on the ratio of indices between the transparent
material entered and the material exited, in practice, the higher the
index of refraction, the more the light is bent. Typical values are 1.0
for air, 1.33 for water, and 1.44 for glass.
 Values from 0.50 to 1.00 simulate refraction
underwater.
Values from 0.50 to 1.00 simulate refraction
underwater.
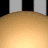
Transparency
Controls the degree to which a material allows light to pass through.
|
Opaque |
Middle |
Transparent |
|
|

|

|
Translucency
Controls the degree to which the material is able to filter and diffuse
light.
|
Opaque |
Middle |
Transparent |
|

|

|

|
 Increasing the translucency value gives the
material more back lighting.
Increasing the translucency value gives the
material more back lighting.
Density of holes
Controls the size and the density of the holes of the mesh in corroded
or eroded appearances.
Metallic
Mix
Controls the metallic quality of a material. Set to 0,
it produces a glossy finish; set to 1,
it produces a more metallic finish.
Roughness
Controls the size (coarseness) of any highlights on a surface. It is
also known as the specular exponent.
Scale
Controls the size of the metallic flakes in the metallic layer.
Amplitude
Controls the amplitude of the metallic flakes. When set to smaller values,
the metallic flakes are flat. When set to larger values, the metallic
flakes are irregular and high.
Metallic flake material
Controls selection between different metallic layers applied to the
material.
|
Aluminum |
Copper |
Gold |
Silver |
|

|

|

|

|
Anisotropic
PhotoWorks models anisotropic
reflection by laying (virtual) cylinders along the surface.
 Not all appearances have anisotropic properties.
For example, brushed aluminum looks different when seen in the brushing
direction than when seen perpendicular to the brushing direction.
Not all appearances have anisotropic properties.
For example, brushed aluminum looks different when seen in the brushing
direction than when seen perpendicular to the brushing direction.
Floor Height
Controls the height difference between neighboring cylinders.
 For a stronger anisotropic effect, decrease
the Floor height.
For a stronger anisotropic effect, decrease
the Floor height.
Cylinder distance
Controls the distance between the cylinders.
 For a stronger anisotropic effect, increase
the Cylinder distance.
For a stronger anisotropic effect, increase
the Cylinder distance.
Bias
Makes the effect of light on the surface stronger in the horizontal
or vertical direction.
|
Horizontal |
Middle |
Vertical |
|

|

|

|
 This property is available only for Woven Anisotropic appearances.
This property is available only for Woven Anisotropic appearances.
Related Topics
Appearances
PropertyManager Color/Image tab
Appearances
PropertyManager Mapping tab
Appearances
PropertyManager Surface Finish tab