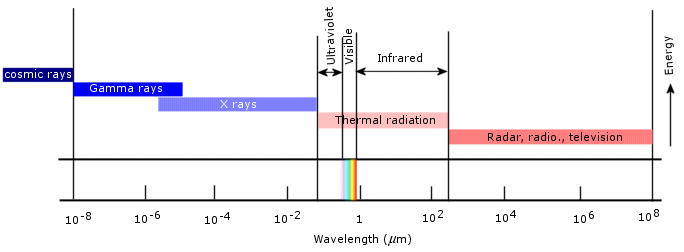
Thermal radiation is the thermal energy emitted by bodies in the form of electromagnetic waves because of their temperature. All bodies with temperatures above the absolute zero emit thermal energy. Because electromagnetic waves travel in vacuum, no medium is necessary for radiation to take place. The following figure shows the range, in wavelength, of thermal radiation compared to radiation emitted by other means (X-rays, γ-rays, cosmic rays, etc).
The thermal energy of the sun reaches the earth by radiation. Because electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, radiation is the fastest heat transfer mechanism.