During a Topology Optimization, the program starts with the given maximum
physical space of a component, which includes all elements, and through an iterative process
determines a new material distribution that leads to a lighter yet stiff shape.
When the
iterative optimization process completes, you view the optimized shape of the component
in a
Material Mass Plot.
To open a
Material Mass
plot:
- In a Topology study tree under Results, double-click
Material Mass.
Display
Elements with low relative mass
densities (less than 0.3) are considered soft elements. These elements do not contribute
to the overall stiffness of the component, and they can be safely removed. Elements with
high relative mass densities (larger than 0.7), are considered solid. These elements
contribute the most to the overall stiffness (as a measure of the load carrying
capacity) of the component, and they remain intact in the final design. An isovalue
slider adjusts the inclusion of elements in the
Material Mass
plot according to their relative mass density values.
| |
Default |
The Default
position of the isovalue slider removes those elements with relative
mass density values less than 0.3. |
| |
Material Mass -
Heavy
|
Moving the slider towards
Heavy includes all elements. |
| |
Material - Mass Light
|
Moving the slider towards
Light includes only the solid elements
(with relative mass density 1.0) that cannot be removed. Elements selected by the algorithm as
Must Keep elements are yellow.
Elements selected as Ok to Remove (with
relative mass density less than 0.3) are deep purple. The
default color options of the Material
Mass plot are selected to better assist people
with color-blindness. The default setting for is Optimized for Material
Mass. You can select a custom color map under
User defined.
|
 |
Show Material Mass
Plot
|
Generates the Material
Mass plot based on the current slider position. You
can view the calculated total mass of the elements in the
Material Mass plot below the slider (as
absolute value and as percentage of the original mass). |
| |
Calculate Smoothed
Mesh
|
Creates a smoother surface mesh
from the active Material Mass Plot (removes
or modifies elements that create jagged edges and sharp
angles). To save the smoothed mesh data of
the optimized part as new geometry, right-click the
Material Mass plot, and click
Export Smoothed Mesh. You can save
the mesh data in a new configuration, or in a new part
file.
Advanced Mesh Smoothing
Options:
|
Coarse
|
The smoothing of the surfaces is
performed in cycles. Moving the slider to
Coarse applies only one
smoothing cycle to the Material
Mass plot.
|
|
Smooth
|
Moving the slider to
Smoothapplies higher number
of smoothing cycles, and increases the computation
time.
|
|
Specify color for Smoothed Mesh
|
Select to specify a color for the
smoothed mesh geometry. Default option is the part
color.
|
|
Property
| |
Include title text
|
Type a title for the plot. |
| |
Associate plot with name view orientation
|
Associates a predefined view orientation with the
active plot. |
A
Material Mass plot of an optimized car hood
component is shown. The soft elements are removed from the original geometry (maximum
physical space).
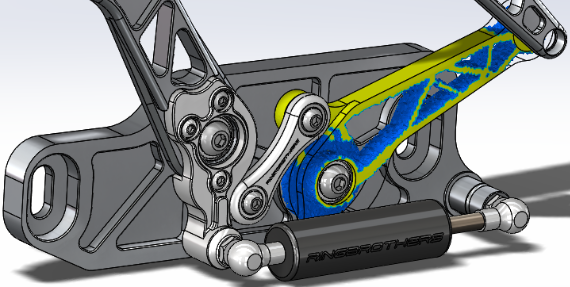
(Image courtesy of Ring Brothers LLC.)