You can
use
the Min Max formulation in a Topology study when multiple load cases act on a
component.
When you subject a component to multiple load cases, the Min Max
formulation for the optimization goal Best Stiffness to Weight
ratio seeks to maximize the component stiffness, or minimize its compliance, for
each load case independently.
For example, for a component subjected to three independent load cases,
the standard optimization formulation for Best Stiffness to
Weight ratio for a given mass reduction constraint seeks to minimize the
total compliance. Compliance is a measure of the overall flexibility or softness of a
structure, and is the reciprocal of stiffness. The total compliance is the sum of the
three
compliances,
C1, C2, and C3, calculated independently for each load case.
|
|
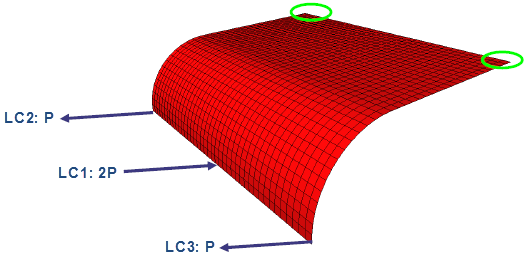
| Shell mesh model of a plate loaded with three
independent load cases: LC1, LC2, and LC3. The six degrees of freedom at
the corners are fixed. |
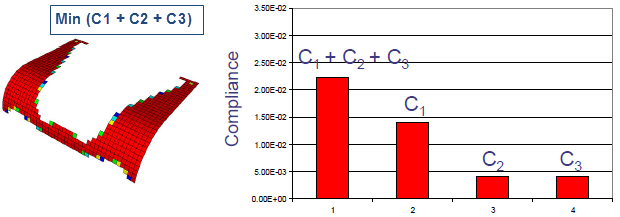 |
| Optimized shape from standard formulation.
Optimization Objective Min (C1 + C2 +C3) under a 40% mass reduction
constraint. |
The Min Max optimization formulation seeks to minimize the maximum
compliance calculated independently from the load cases and maximize the component’s
stiffness for each load case. The optimized shape of the component has the maximum
stiffness for each load case that can act independently.
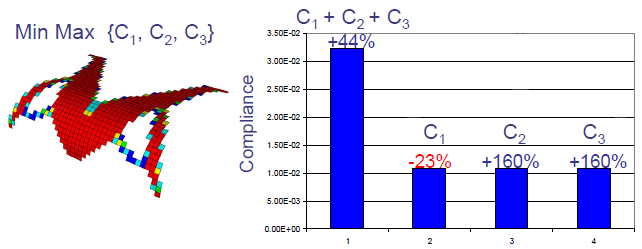 |
| Optimized shape from Min Max formulation.
Optimization Objective Min Max {C1 + C2 +C3} under a 40% mass
reduction constraint. Optimized shape has equal stiffness for each
independent load case. |
Recommendation: To resolve any convergence issues when using the Min
Max formulation, select .