| Blackbody |
Ideal radiator, emits and absorbs the maximum possible amount of radiation at any temperature and wavelength. An example of a blackbody is a small opening in a heated cavity. |
| Irradiation |
Rate at which radiation is incident on a surface from all directions per unit area. |
| Radiosity |
Rate at which radiation leaves a surface due to emission and reflection in all directions per unit area of the surface. |
| Absorptivity (α) |
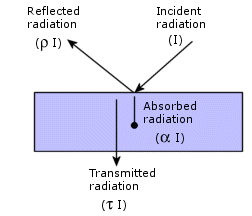
Fraction of incident radiation absorbed by the surface. |
| Reflectivity (ρ) |
Fraction of incident radiation reflected by the surface.
Reflectivity of a black body is zero.
|
| Transmissivity (τ)
|
Fraction of incident radiation transmitted by the surface.
The software assumes that the transmissivity is zero.
The following relation relates absorptivity, reflectivity, and transmissivity of a surface: α + ρ + τ = 1.
 |
| Emissive Power (E) |
Rate of radiation emitted by a surface in all directions per unit area of the surface. The unit of E is W/m2.
|
| Emissivity (ε) |
Ratio of the emissive power of a surface to the emissive power of a blackbody at the same temperature.
ε = E/Eb
where Eb is the emissive power of a blackbody at the same temperature. The emissivity of a surface is a function of temperature.
|