| |
Standard mesh |
Activates the Voronoi-Delaunay
meshing scheme for subsequent meshing operations. |
| |
Curvature-based mesh |
Activates the curvature-based meshing scheme for
subsequent meshing operations. The mesher creates more elements
in higher-curvature areas automatically (without need for mesh
control). The
Curvature-based mesher supports multi-threaded surface and
volume meshing for assembly and multibody part documents.
The Standard mesher supports only multi-threaded volume
meshing.
|
| |
Blended
curvature-based mesh |
Activates the Blended curvature-based meshing scheme.
This mesher automatically adapts the element size to the local
curvature of the geometry to create a smooth mesh pattern. Use
the Blended curvature-based mesher for models that failed to
mesh with the Standard or Curvature-based mesher. There are cases where the Blended
curvature-based mesher can overcome mesh failure, generating
a solid mesh with higher-quality elements (lower Jacobian
and Aspect ratios) than the Standard or the Curvature-based
meshers.
The table lists the
Simulation licenses that support single-core processing and
multicore processing for the Blended curvature-based
mesher.
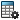
| Licenses with Single-core
Processing |
Licenses with Multicore
Processing |
- Simulation Xpress
- Simulation in SOLIDWORKS
Premium
- SOLIDWORKS Simulation
Standard
The meshing process can be slower when
running on a single central processor unit
(CPU). |
- SOLIDWORKS Simulation
Professional
- SOLIDWORKS Simulation
Premium
There is no limit to the number of physical
cores that the Blended curvature-based mesher can
access. |
The local mesh control
settings for the maximum element size and minimum element
size should be within the range defined by the Maximum element size and
Minimum element
size of the global mesh settings. If the
local mesh control settings fall outside the range defined
by the global mesh settings for maximum and minimum element
sizes, mesh control is not enforced. Also, the enforcement of the Minimum number of elements in a
circle setting depends on the resulting
element size on the curved geometry being within the
range defined by the minimum and maximum element sizes
of the global mesh settings.
Click Calculate Minimum
Element Size to let the program
calculate the optimal value for the minimum element
size.
The Blended curvature-based mesher does
not support a continuous mesh (common nodes between
touching boundaries) for bonded sets. Mesh controls are
not transferable between touching boundaries of bodies
that mesh independently and are bonded. For example, you
may need to apply mesh controls separately to the
touching edges of two bodies that are bonded.
|
 |
Calculate Minimum
Element Size |
Available for the Blended curvature-based mesher
only. Calculates the minimum element size based on either the
minimum radius of geometric curvature, or the minimum element
value set for mesh control.
- Include
minimum radius of curvature from
geometry
- Include
minimum element size from mesh
control
When you select both options, the program selects the
minimum of the two element size values. Click Apply to
accept the calculated minimum element size.
|
 |
Unit |
Sets units for mesh sizes and
tolerance. |
 |
Global Size |
Available for standard mesh only. Sets the global
average element size. The software suggests a default value
based on the model volume and surface area. |
| |
Tolerance |
Available for standard mesh only. Sets the tolerance
value. The program calculates the mesh tolerance value as the
minimum of these quantities:
- 5% of the global element size (default
value)
- 30% of the smallest mesh element size
defined for mesh control definitions in the Mesh Control
PropertyManager
- The user-defined mesh tolerance value
in the Mesh
PropertyManager (if the user enters a value smaller than
the default mesh tolerance value)
If the distance between two nodes is smaller than this
value, the nodes are merged unless otherwise specified by
contact conditions. Adjusting the tolerance can help resolve some meshing
problems. For example, if meshing fails because of free
edges, increasing the tolerance can solve the
problem.
|
| |
Automatic transition |
Available for standard mesh
only. When checked, the program automatically applies mesh
controls to small features, holes, fillets, and other fine
details of your model. Clear Automatic transition before meshing large
models with many small features and details to avoid generating
large numbers of elements. See example below. |
 |
Maximum element size |
Available for the curvature-based meshers only. The
maximum element size is used for boundaries with lowest
curvature. |
 |
Minimum element size |
Available for the curvature-based meshers only. The
minimum element size is used for boundaries with the highest
curvature. |
 |
Min number of elements in a circle |
Available for the curvature-based meshers only. Determines the element size by the minimum
number of elements that fit in a hypothetical circle.
For
the Blended curvature-based mesher, the computed element size
must be between the Maximum element
size and Minimum
element size. For the Curvature-based mesher,
this setting is enforced even if the computed element size is
outside the range defined by the Maximum element size and Minimum element size.See How Element Size Is
Determined.
|
 |
Element size growth ratio |
Available for curvature-based meshers only. Specifies
the global element size growth ratio starting from regions of
high curvatures in all directions. |