Motors are Motion Study elements that move components in an assembly by simulating the effects of various types of motors.
To open the Motor PropertyManager:
From an assembly, click Motor
 (MotionManager toolbar).
(MotionManager toolbar).
Motor Type
 |
Rotary Motor |
Specifies a rotary
motor. |
 |
Linear Motor (Actuator) |
Specifies a linear
motor. |
 |
Path Mate Motor (Motion Analysis only) |
For a selected path mate in
the assembly, specifies displacement, velocity, or acceleration
as a body moves along a path. |
Mate/Direction
 |
Path Mate |
Selects the path mate that
defines the path of motion. |
 |
Reverse Direction |
Reverses the direction of motion.
|
 |
Component |
Selects the component relative to which the
motion is applied.
|
Component/Direction
 |
Motor Location |
Selects a feature at which to
locate the motor. |
 |
Reverse Direction |
Reverses the direction of motion.
|
| |
Motor Direction |
Selects the feature, such as a
face or an
edge
that defines the directional axis of the motor. |
 |
Component |
Selects the component relative to which the
motion is applied.
|
Motion
| Constant speed |
Specifies a constant speed motor.
- Speed
 Sets the speed of a constant speed
motor.
|
| Distance |
Specifies that the motor operates for a set distance
and time frame.
- Displacement
 Sets the distance of operation for a distance
motor.
- Start time
 Sets the start time for the operation of a
distance motor.
- Duration time
 Sets the time duration of operation of a
distance motor
|
| Oscillating |
Specifies an oscillating motor profile.
- Displacement
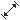 Sets an offset profile amplitude for an
oscillating motor.
- Frequency
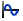 Sets the profile frequency for an oscillating
motor.
- Phase Shift
 Sets the profile phase shift for an oscillating
motor.
|
| Servo Motor (Motion Analysis only) |
Specifies a servo motor that you can use for
event-based motion studies.
- Displacement
Specifies a displacement
servo motor.
- Velocity
Specifies a velocity servo
motor.
- Acceleration
Specifies an
acceleration servo motor.
|
| Segments |
In
the Function Builder dialog box, selects
the component relative to which the motion is
applied. Defines
profile from piecewise continuous functions of time or cycle
angle.
|
| Data Points |
In
the Function Builder dialog box,
defines
a profile from an interpolated data set as a function of
time, cycle angle, or motion study results.
|
| Expression |
In
the Function Builder dialog box,
defines
a profile as a mathematical expression of time, cycle angle,
or motion study results.
|
| Load Function from File |
Importings
a
function created with the Function Builder from a
.sldfcn file.
|
| Delete Functions |
In
the Delete Motion
Functions dialog box, deletes
functions
created with the
Function
Builder. |
| Edit |
Permits editing of selected profile
type.
|
More Options
Use this section to set motion relative to another part, and to
select components for load-bearing faces or edges to transfer them to SOLIDWORKS
Simulation.
 |
Load-bearing Faces/Edges |
Specifies the load-bearing
faces or edges. |
Notes
Motors move components in a selected direction, but they are not
forces. Motor strength does not vary based on component size or mass. For example, a
small cube moves at the same speed as a large cube if you set the velocity of the
motor to a given value in both cases.
If something causes the reference point of the motor direction to
change, the motor continues to move the component in the new direction. This can
occur, for example, if there is a collision between the component that is moved by
the motor and another component.
Do not add more than one motor of the same type to the same
component.
Motion
from
motors supersedes motion
from
any other simulation element. If you have a motor moving a component to the left,
and a spring pulling a component to the right, the component moves to the left,
while the power consumption of the motor increases.