Nonlinear Static Analysis
Linear static analysis assumes that the relationship between loads and
the induced response is linear. For example, if you double the magnitude
of loads, the response (displacements, strains, stresses, reaction forces,
etc.), will also double.
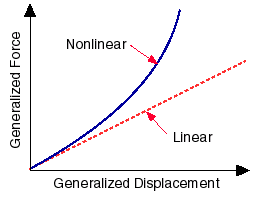
All real structures behave nonlinearily in one way or another at some
level of loading. In some cases, linear analysis may be adequate. In many
other cases, the linear solution can produce erroneous results because
the assumptions upon which it is based are violated. Nonlinearity can
be caused by the material behavior, large displacements, and contact conditions.
You can use a nonlinear study to solve a linear problem. The results
can be slightly different due to different procedures.
In the nonlinear static analysis, dynamic effects like inertial and
damping forces are not considered. Processing a nonlinear study differs
from processing a static study in the following ways:
Study Properties
Material
Loads and Restraints
Solution
Results
Contact Problems
In this section, you will learn about the following topics: