The Rainflow cycle counting method extracts the composition of a variable amplitude load history. The software implements the method as follows:
- Extract peaks and troughs from the load history.
- Make the amplitudes of the first and last data points the same by appending a data point if necessary.
- Detect the highest peak and reorder the data such that the highest peak becomes the first and last points.
- Start counting the peaks as follows:
- Consider the first four peaks and troughs ( 1, 2, 3, and 4). A Rainflow cycle is counted if the second segment is vertically shorter than the first and the third segments (i.e. b is smaller than a and c).
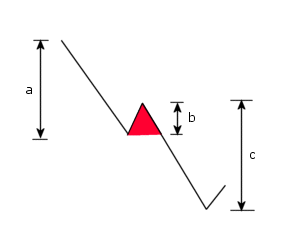
- If a cycle is counted, the program starts from the beginning of the record ignoring peaks that have already been counted. If no peak is counted, the program checks the next group of peaks (peaks 2, 3, 4, and 5) and the process continues. At the end, each peak and each trough corresponds to a Rainflow cycle.
- Ignore and load cycles that are below the percentage specified in the properties of the study.
- Divide the alternating and mean stress ranges into the number of bins specified in the properties of the study. You can view the results by viewing the Rainflow matrix chart.
Application of the Rainflow Cycle Counting Method
| Fast Counting |
Fast counting is used when the fatigue study refers to one static study and has only one variable-amplitude event. In this case, the program extracts bins directly from the original record. It then evaluates the damage resulting from each bin at each node and calculates the accumulative damage. |
| Full Analysis |
When multiple variable-amplitude events are used, the program calculates the stresses at each point in time for each variable-amplitude record at every node. At each node, the program combines the stresses and extracts the Rainflow bins that are then used to evaluate the damage.
Full analysis is also used when a variable amplitude record is associated with more than one study with the different shifts or intervals.
|